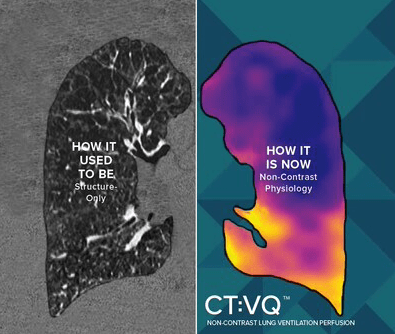
The solution converts standard non-contrast chest CTs into quantitative lung function maps and has also received CMS reimbursement confirmation.
4DMedical has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for CT:VQ, a non-contrast, ventilation-perfusion (VQ) imaging solution. Concurrently, the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has confirmed reimbursement for the technology under Category III CPT codes, adding to the existing reimbursement for the underlying chest CT scan.
CT:VQ is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform that processes standard, non-contrast chest CT scans to produce quantitative maps of lobar ventilation and perfusion. The system is designed to integrate directly into routine radiology workflows using DICOM and PACS reporting. It leverages a facility’s existing CT scanners, allowing hospitals to provide functional lung imaging without investing in new capital equipment or having nuclear medicine capacity.
“With FDA clearance and Medicare payment in place, any hospital with a CT scanner can turn a routine chest CT into a high-resolution ventilation-perfusion study in minutes, without new hardware or workflow complexity,” says Andreas Fouras, PhD, founder and CEO of 4DMedical, in a release.
Expanding Access Without New Hardware
The technology allows a standard non-contrast chest CT to serve as a reimbursable V/Q study. According to the company, this streamlines the process for patients, who can complete the scan in a single appointment without the need for injections. Radiologists receive high-resolution V/Q maps directly in PACS, providing information for PE workups, CTEPH assessment, and COPD phenotyping.
By operating on existing scanners, the technology can be implemented in hospitals and imaging centers to expand VQ imaging access, particularly for community and rural patients in facilities that lack nuclear medicine departments. More than 1 million nuclear V/Q scans are performed in the US annually. 4DMedical notes that its clinical validation for CT:VQ included performance testing against SPECT and expert reader studies. Early clinical partners in the US include Stanford University and Brooke Army Medical Center.
Photo caption: CT:VQ
Photo credit: 4DMedical