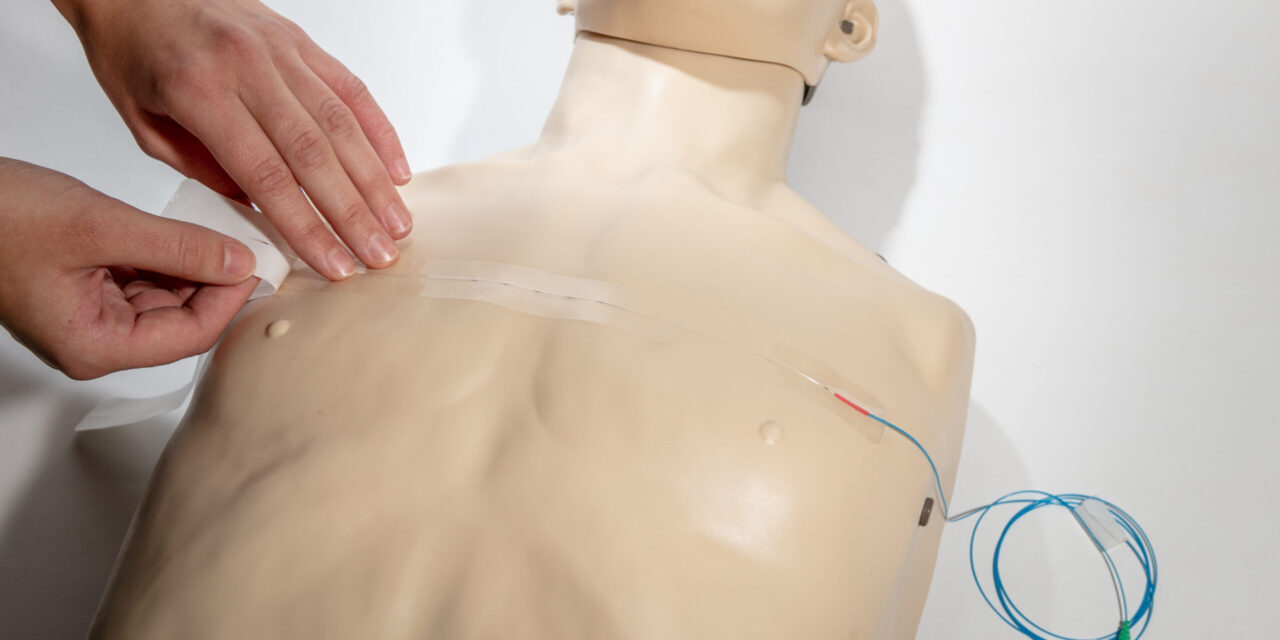
The newly cleared system uses a disposable sensor and software to track breathing motion in real-time during image-guided radiation therapy.
EmpNia announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance to market its product, eMotus—a disposable sensor pad and software for managing respiratory motion in image-guided radiation therapy—to hospitals and cancer centers throughout the United States.
Managing respiratory motion remains a critical challenge in delivering safe and precise image-guided radiation therapy. Existing solutions in the market are often difficult to use, disruptive to clinical workflow, ineffective for many patient presentations, incompatible across various imaging and therapy modalities, and capital-intensive to install and maintain, according to a press release from EmpNia.
EmpNia’s eMotus system is designed to overcome these barriers with a single-use disposable sensor pad and software that provides real-time respiratory motion tracking for all patient types. Universally compatible with existing imaging and therapy equipment, eMotus aims to enable clinics to adopt state-of-the-art motion management without costly infrastructure investments.
“Effectively managing respiratory motion across all patient types and delivery systems, whether during imaging or radiation therapy, has long challenged clinicians and added unnecessary time and complexity,” says Cliff Robinson, MD, chief medical officer of EmpNia, in a release. “eMotus overcomes these challenges with a simple, reliable, and universally compatible solution that lets care teams stay focused on treating patients, not managing equipment.”
In pre-market evaluations, eMotus demonstrated significant improvements in workflow efficiency, setup simplicity, and motion tracking accuracy across all clinical presentations. The eMotus system is intended for use by radiation oncology professionals managing patients undergoing image-guided radiation therapy who require monitoring and management of respiratory motion during treatment.
Photo caption: eMotus shown in use
Photo credit: EmpNia